Azure SQL Managed Instance is the intelligent, scalable cloud database service that combines the broadest SQL Server database engine compatibility with all the benefits of a fully managed and evergreen platform as a service. SQL Managed Instance has near 100% compatibility with the latest SQL Server (Enterprise Edition) database engine, providing a native virtual network (VNet) implementation that addresses common security concerns, and a business model favorable for existing SQL Server customers. SQL Managed Instance allows existing SQL Server customers to lift and shift their on-premises applications to the cloud with minimal application and database changes. At the same time, SQL Managed Instance preserves all PaaS capabilities (automatic patching and version updates, automated backups, high availability) that drastically reduce management overhead and TCO.
If you're new to Azure SQL Managed Instance, check out the Azure SQL Managed Instance video from our in-depth Azure SQL video series:
Important
For a list of regions where SQL Managed Instance is currently available, see Supported regions.
The following diagram outlines key features of SQL Managed Instance:
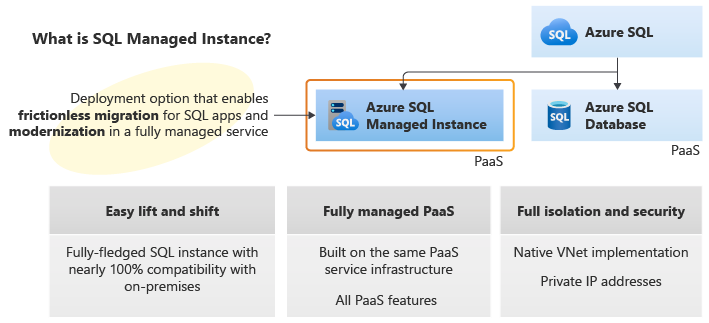
Azure SQL Managed Instance is designed for customers looking to migrate a large number of apps from an on-premises or IaaS, self-built, or ISV provided environment to a fully managed PaaS cloud environment, with as low a migration effort as possible. Using the fully automated Azure Data Migration Service, customers can lift and shift their existing SQL Server instance to SQL Managed Instance, which offers compatibility with SQL Server and complete isolation of customer instances with native VNet support. For more information on migration options and tools, see Migration overview: SQL Server to Azure SQL Managed Instance.
With Software Assurance, you can exchange your existing licenses for discounted rates on SQL Managed Instance using the Azure Hybrid Benefit for SQL Server. SQL Managed Instance is the best migration destination in the cloud for SQL Server instances that require high security and a rich programmability surface.
Key features and capabilities
SQL Managed Instance combines the best features that are available both in Azure SQL Database and the SQL Server database engine.
Important
SQL Managed Instance runs with all of the features of the most recent version of SQL Server, including online operations, automatic plan corrections, and other enterprise performance enhancements. A comparison of the features available is explained in Feature comparison: Azure SQL Managed Instance versus SQL Server.
| PaaS benefits | Business continuity |
|---|---|
| No hardware purchasing and management No management overhead for managing underlying infrastructure Quick provisioning and service scaling Automated patching and version upgrade Integration with other PaaS data services | 99.99% uptime SLA Built-in high availability Hybrid Disaster recovery with failover (preview) between SQL Managed Instance and SQL Server 2022. Data protected with automated backups < Customer configurable backup retention period User-initiated backups that can be restored to SQL Server 2022 Point-in-time database restore capability |
| Security and compliance | Management |
| Isolated environment (VNet integration, single tenant service, dedicated compute and storage) Transparent data encryption (TDE) Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) authentication, single sign-on support Azure AD server principals (logins) What is Windows Authentication for Azure AD principals (Preview) Adheres to compliance standards same as Azure SQL Database SQL auditing Advanced Threat Protection | Azure Resource Manager API for automating service provisioning and scaling Azure portal functionality for manual service provisioning and scaling Data Migration Service |
Important
Azure SQL Managed Instance has been certified against a number of compliance standards. For more information, see the Microsoft Azure Compliance Offerings, where you can find the most current list of SQL Managed Instance compliance certifications, listed under SQL Database.
The key features of SQL Managed Instance are shown in the following table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| SQL Server version/build | SQL Server database engine (latest stable) |
| Managed automated backups | Yes |
| Built-in instance and database monitoring and metrics | Yes |
| Automatic software patching | Yes |
| The latest database engine features | Yes |
| Number of data files (ROWS) per the database | Multiple |
| Number of log files (LOG) per database | 1 |
| VNet - Azure Resource Manager deployment | Yes |
| VNet - Classic deployment model | No |
| Portal support | Yes |
| Built-in Integration Service (SSIS) | No - SSIS is a part of Azure Data Factory PaaS |
| Built-in Analysis Service (SSAS) | No - SSAS is separate PaaS |
| Built-in Reporting Service (SSRS) | No - use Power BI paginated reports instead or host SSRS on an Azure VM. While SQL Managed Instance cannot run SSRS as a service, it can host SSRS catalog databases for a reporting server installed on Azure Virtual Machine, using SQL Server authentication. |
vCore-based purchasing model
The vCore-based purchasing model for SQL Managed Instance gives you flexibility, control, transparency, and a straightforward way to translate on-premises workload requirements to the cloud. This model allows you to change compute, memory, and storage based upon your workload needs. The vCore model is also eligible for up to 55 percent savings with the Azure Hybrid Benefit for SQL Server.
In the vCore model, you can choose hardware configurations as follows:
- Standard Series (Gen5) logical CPUs are based on Intel® E5-2673 v4 (Broadwell) 2.3 GHz, Intel® SP-8160 (Skylake), and Intel® 8272CL (Cascade Lake) 2.5 GHz processors, with 5.1 GB of RAM per CPU vCore, fast NVMe SSD, hyper-threaded logical core, and compute sizes between 4 and 80 cores.
- Premium Series logical CPUs are based on Intel® 8370C (Ice Lake) 2.8 GHz processors, with 7 GB of RAM per CPU vCore, fast NVMe SSD, hyper-threaded logical core, and compute sizes between 4 and 80 cores.
- Premium Series Memory-Optimized logical CPUs are based on Intel® 8370C (Ice Lake) 2.8 GHz processors, with 13.6 GB of RAM per CPU vCore, fast NVMe SSD, hyper-threaded logical core, and compute sizes between 4 and 64 cores.
Find more information about the difference between hardware configurations in SQL Managed Instance resource limits.
Service tiers
SQL Managed Instance is available in two service tiers:
- General purpose: Designed for applications with typical performance and I/O latency requirements.
- Business Critical: Designed for applications with low I/O latency requirements and minimal impact of underlying maintenance operations on the workload.
Both service tiers guarantee 99.99% availability and enable you to independently select storage size and compute capacity. For more information on the high availability architecture of Azure SQL Managed Instance, see High availability and Azure SQL Managed Instance.
General Purpose service tier
The following list describes key characteristics of the General Purpose service tier:
- Designed for the majority of business applications with typical performance requirements
- High-performance Azure Blob storage (16 TB)
- Built-in high availability based on reliable Azure Blob storage and Azure Service Fabric
For more information, see Storage layer in the General Purpose tier and Storage performance best practices and considerations for SQL Managed Instance (General Purpose).
Find more information about the difference between service tiers in SQL Managed Instance resource limits.
Business Critical service tier
The Business Critical service tier is built for applications with high I/O requirements. It offers the highest resilience to failures using several isolated replicas.
The following list outlines the key characteristics of the Business Critical service tier:
- Designed for business applications with highest performance and HA requirements
- Comes with super-fast local SSD storage (up to 4 TB on Standard Series (Gen5), up to 5.5 TB on Premium Series and up to 16 TB on Premium Series Memory-Optimized)
- Built-in high availability based on Always On availability groups and Azure Service Fabric
- Built-in additional read-only database replica that can be used for reporting and other read-only workloads
- In-Memory OLTP that can be used for workload with high-performance requirements
Find more information about the differences between service tiers in SQL Managed Instance resource limits.
Management operations
Azure SQL Managed Instance provides management operations that you can use to automatically deploy new managed instances, update instance properties, and delete instances when no longer needed. Detailed explanation of management operations can be found on managed instance management operations overview page.
Advanced security and compliance
SQL Managed Instance comes with advanced security features provided by the Azure platform and the SQL Server database engine.
Security isolation
SQL Managed Instance provides additional security isolation from other tenants on the Azure platform. Security isolation includes:
- Native virtual network implementation and connectivity to your on-premises environment using Azure ExpressRoute or VPN Gateway.
- In a default deployment, the SQL endpoint is exposed only through a private IP address, allowing safe connectivity from private Azure or hybrid networks.
- Single-tenant with dedicated underlying infrastructure (compute, storage).
The following diagram outlines various connectivity options for your applications:

To learn more details about VNet integration and networking policy enforcement at the subnet level, see VNet architecture for managed instances and Connect your application to a managed instance.
Important
Place multiple managed instances in the same subnet, wherever that is allowed by your security requirements, as that will bring you additional benefits. Co-locating instances in the same subnet will significantly simplify networking infrastructure maintenance and reduce instance provisioning time, since a long provisioning duration is associated with the cost of deploying the first managed instance in a subnet.
Security features
Azure SQL Managed Instance provides a set of advanced security features that can be used to protect your data.
- SQL Managed Instance auditing tracks database events and writes them to an audit log file placed in your Azure storage account. Auditing can help you maintain regulatory compliance, understand database activity, and gain insight into discrepancies and anomalies that could indicate business concerns or suspected security violations.
- Data encryption in motion - SQL Managed Instance secures your data by providing encryption for data in motion using Transport Layer Security. In addition to Transport Layer Security, SQL Managed Instance offers protection of sensitive data in flight, at rest, and during query processing with Always Encrypted. Always Encrypted offers data security against breaches involving the theft of critical data. For example, with Always Encrypted, credit card numbers are stored encrypted in the database always, even during query processing, allowing decryption at the point of use by authorized staff or applications that need to process that data.
- Advanced Threat Protection complements auditing by providing an additional layer of security intelligence built into the service that detects unusual and potentially harmful attempts to access or exploit databases. You are alerted about suspicious activities, potential vulnerabilities, and SQL injection attacks, as well as anomalous database access patterns. Advanced Threat Protection alerts can be viewed from Microsoft Defender for Cloud. They provide details of suspicious activity and recommend action on how to investigate and mitigate the threat.
- Dynamic data masking limits sensitive data exposure by masking it to non-privileged users. Dynamic data masking helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data by enabling you to designate how much of the sensitive data to reveal with minimal impact on the application layer. It's a policy-based security feature that hides the sensitive data in the result set of a query over designated database fields, while the data in the database is not changed.
- Row-level security (RLS) enables you to control access to rows in a database table based on the characteristics of the user executing a query (such as by group membership or execution context). RLS simplifies the design and coding of security in your application. RLS enables you to implement restrictions on data row access. For example, ensuring that workers can access only the data rows that are pertinent to their department, or restricting a data access to only the relevant data.
- Transparent data encryption (TDE) encrypts SQL Managed Instance data files, known as encrypting data at rest. TDE performs real-time I/O encryption and decryption of the data and log files. The encryption uses a database encryption key (DEK), which is stored in the database boot record for availability during recovery. You can protect all your databases in a managed instance with transparent data encryption. TDE is proven encryption-at-rest technology in SQL Server that is required by many compliance standards to protect against theft of storage media.
Migration of an encrypted database to SQL Managed Instance is supported via Azure Database Migration Service or native restore. If you plan to migrate an encrypted database using native restore, migration of the existing TDE certificate from the SQL Server instance to SQL Managed Instance is a required step. For more information about migration options, see SQL Server to Azure SQL Managed Instance Guide.
Azure Active Directory integration
SQL Managed Instance supports traditional SQL Server database engine logins and logins integrated with Azure AD. Azure AD server principals (logins) are an Azure cloud version of on-premises database logins that you are using in your on-premises environment. Azure AD server principals (logins) enable you to specify users and groups from your Azure AD tenant as true instance-scoped principals, capable of performing any instance-level operation, including cross-database queries within the same managed instance.
A new syntax is introduced to create Azure AD server principals (logins), FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER. For more information on the syntax, see CREATE LOGIN, and review the Provision an Azure Active Directory administrator for SQL Managed Instance article.
Azure Active Directory integration and multi-factor authentication
SQL Managed Instance enables you to centrally manage identities of database users and other Microsoft services with Azure Active Directory integration. This capability simplifies permission management and enhances security. Azure Active Directory supports multi-factor authentication to increase data and application security while supporting a single sign-on process.
Authentication
SQL Managed Instance authentication refers to how users prove their identity when connecting to the database. SQL Managed Instance supports three types of authentication:
SQL Authentication:
This authentication method uses a username and password.
Azure Active Directory Authentication:
This authentication method uses identities managed by Azure Active Directory and is supported for managed and integrated domains. Use Active Directory authentication (integrated security) whenever possible.
Windows Authentication for Azure AD Principals:
Kerberos authentication for Azure AD Principals enables Windows Authentication for Azure SQL Managed Instance. Windows Authentication for managed instances empowers customers to move existing services to the cloud while maintaining a seamless user experience and provides the basis for infrastructure modernization.
Authorization
Authorization refers to what a user can do within a database in Azure SQL Managed Instance, and is controlled by your user account's database role memberships and object-level permissions. SQL Managed Instance has the same authorization capabilities as SQL Server 2017.
Database migration
SQL Managed Instance targets user scenarios with mass database migration from on-premises or IaaS database implementations. SQL Managed Instance supports several database migration options that are discussed in the migration guides. See Migration overview: SQL Server to Azure SQL Managed Instance for more information.
Backup and restore
The migration approach leverages SQL backups to Azure Blob storage. Backups stored in Azure Blob Storage can be directly restored into a managed instance using the T-SQL RESTORE command.
- For a quickstart showing how to restore the Wide World Importers - Standard database backup file, see Restore a backup file to a managed instance. This quickstart shows that you have to upload a backup file to Azure Blob Storage and secure it using a shared access signature (SAS).
- For information about restore from URL, see Native RESTORE from URL.
Important
Backups from a managed instance can only be restored to other managed instances, or to SQL Server 2022. They cannot be restored to other versions of SQL Server, or to Azure SQL Database.
Database Migration Service
Azure Database Migration Service is a fully managed service designed to enable seamless migrations from multiple database sources to Azure data platforms with minimal downtime. This service streamlines the tasks required to move existing third-party and SQL Server databases to Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Managed Instance, and SQL Server on Azure VM. See How to migrate your on-premises database to SQL Managed Instance using Database Migration Service.
SQL features supported
SQL Managed Instance aims to deliver close to 100% surface area compatibility with the latest SQL Server version through a staged release plan. For a features and comparison list, see SQL Managed Instance feature comparison, and for a list of T-SQL differences in SQL Managed Instance versus SQL Server, see SQL Managed Instance T-SQL differences from SQL Server.
SQL Managed Instance supports backward compatibility to SQL Server 2008 databases. Direct migration from SQL Server 2005 database servers is supported, and the compatibility level for migrated SQL Server 2005 databases is updated to SQL Server 2008.
The following diagram outlines surface area compatibility in SQL Managed Instance:
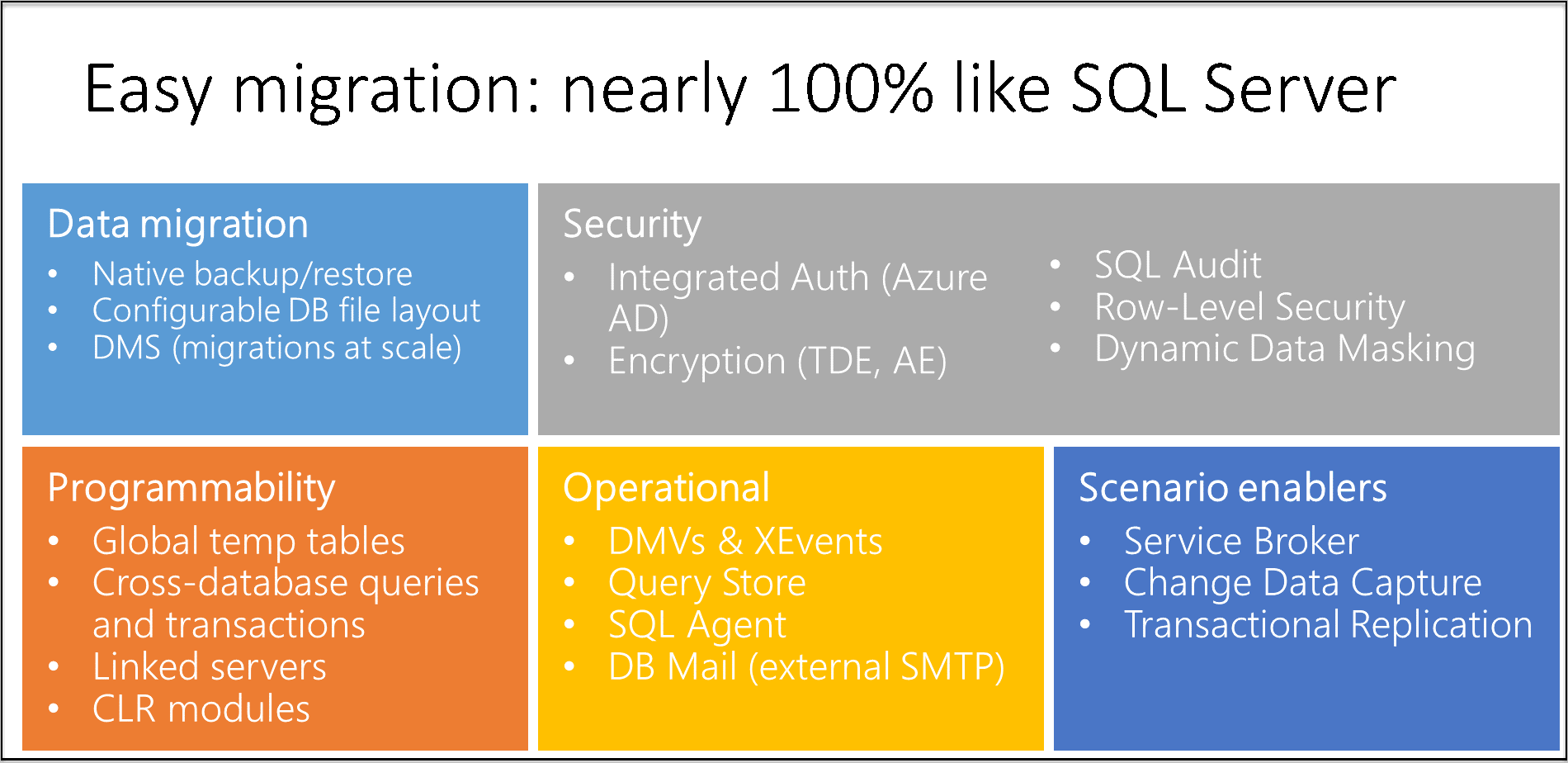
Key differences between SQL Server on-premises and SQL Managed Instance
SQL Managed Instance benefits from being always-up-to-date in the cloud, which means that some features in SQL Server may be obsolete, be retired, or have alternatives. There are specific cases when tools need to recognize that a particular feature works in a slightly different way or that the service is running in an environment you do not fully control.
Some key differences:
- High availability is built in and pre-configured using technology similar to Always On availability groups.
- There are only automated backups and point-in-time restore. Customers can initiate
copy-onlybackups that do not interfere with the automatic backup chain. - Specifying full physical paths is unsupported, so all corresponding scenarios have to be supported differently: RESTORE DB does not support WITH MOVE, CREATE DB doesn't allow physical paths, BULK INSERT works with Azure blobs only, etc.
- SQL Managed Instance supports Azure AD authentication and Windows Authentication for Azure Active Directory principals (Preview).
- SQL Managed Instance automatically manages XTP filegroups and files for databases containing In-Memory OLTP objects.
- SQL Managed Instance supports SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) and can host an SSIS catalog (SSISDB) that stores SSIS packages, but they are executed on a managed Azure-SSIS Integration Runtime (IR) in Azure Data Factory. See Create Azure-SSIS IR in Data Factory. To compare the SSIS features, see Compare SQL Database to SQL Managed Instance.
- SQL Managed Instance supports connectivity only through the TCP protocol. It does not support connectivity through named pipes.
Administration features
SQL Managed Instance enables system administrators to spend less time on administrative tasks because the service either performs them for you or greatly simplifies those tasks. For example, OS/RDBMS installation and patching, dynamic instance resizing and configuration, backups, database replication (including system databases), high availability configuration, and configuration of health and performance monitoring data streams.
For more information, see a list of supported and unsupported SQL Managed Instance features, and T-SQL differences between SQL Managed Instance and SQL Server.
Programmatically identify a managed instance
The following table shows several properties, accessible through Transact-SQL, that you can use to detect that your application is working with SQL Managed Instance and retrieve important properties.
Next steps
- To learn how to create your first managed instance, see Quickstart guide.
- For a features and comparison list, see SQL common features.
- For more information about VNet configuration, see SQL Managed Instance VNet configuration.
- For a quickstart that creates a managed instance and restores a database from a backup file, see Create a managed instance.
- For a tutorial about using Azure Database Migration Service for migration, see SQL Managed Instance migration using Database Migration Service.
- For advanced monitoring of SQL Managed Instance database performance with built-in troubleshooting intelligence, see Monitor Azure SQL Managed Instance using Azure SQL Analytics.
- For pricing information, see SQL Database pricing.
No comments:
Post a Comment