To learn more about the benefits of installing a major version upgrade, review each of the following tabs.
Community support
-------–
Every version of PostgreSQL is supported by the community for a defined period of time. During this time, the community releases security patches and bug fixes on a regular cycle. When the version becomes unsupported, the patches and fixes stop on that version.
Performance
--------–
With each new version of PostgreSQL, DB performance improves. Feedback from users is reviewed and considered in the process of designing new innovations.
Security and compliance
--------–
DBs are at high risk of cyberattacks. If an organization fails to upgrade its DB, it can become more vulnerable. Organizations might also have compliance guidelines stating that the application DBs must be up to date with the latest supported versions. For these two reasons alone, PostgreSQL strongly recommends upgrading when available.
Features and extensions
-----------–
Each major upgrade has new features and extensions that can boost performance and add functionality to a DB. Each version establishes new ways of solving known DB issues and introduces DB improvements.
The next sections of the course will cover the step-by-step process for completing a major upgrade.
Specify a Version-Compatible Parameter Group
Step 1: Specify a version-compatible parameter group
Before starting a major upgrade, you should prepare a version-compatible parameter group.
If you are using a custom parameter group, you have two options.
1)You can specify a default parameter group for the new DB engine version.
2) You can create your own custom parameter group for the new DB engine version.
If you associate a new parameter group with a DB instance, reboot the DB after the upgrade completes.
If the DB instance needs to be rebooted to apply the parameter group changes, the instance's parameter group status will show pending-reboot.
You can view an instance's parameter group status in the AWS Management Console or by using a describe operation, such as describe-db-instances.
Check Version Compatibility
Step 2: Check version compatibility
Next, check that your DB's instance class is compatible with the PostgreSQL version to which you are upgrading.
Also, ensure that the target you are upgrading to has a supported upgrade path.
Aurora PostgreSQL upgrades
You can conduct the following Aurora PostgreSQL major version upgrades:
1) Upgrade from version 9.6, minor versions 9.6.9 and later, to version 10, minor versions 10.11 or later.
2) Upgrade from version 10, minor versions 10.7 and later, to version 11, minor versions 11.7 or later.
Check for Unsupported Usage
Step 3: Check for unsupported usage
Next, you need to check for unsupported usage. To do this, access prepared transactions.
Commit or rollback all open prepared transactions before attempting an upgrade.
You can use the following query to verify that there are no open prepared transactions on your instance:
SELECT count(*) FROM pg_catalog.pg_prepared_xacts;
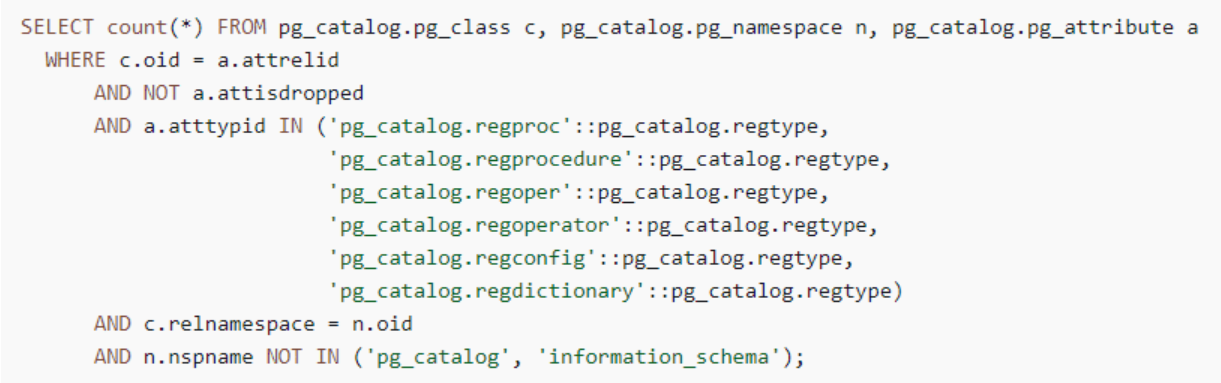
You also need to remove all uses of reg* data types before attempting an upgrade.
With the exception of regtype and regclass, reg* data types cannot be upgraded.
The pg_upgrade utility cannot persist in this data type, which is used to do the upgrade.
To verify that there are no uses of unsupported reg* data types, use the following query for each database.
Handle Amazon RDS Read Replicas or Amazon Aurora Secondary Clusters
PostgreSQL read replicas
During a major version upgrade, Amazon RDS also upgrades all of your in-Region read replicas along with the primary DB instance.
Amazon RDS Step 4: Promote Amazon RDS PostgreSQL read replicas
You cannot upgrade read replicas separately. It could lead to situations where the primary and replica instances have different PostgreSQL major versions.
However, replica upgrades might increase downtime on the primary instance. To prevent a replica upgrade, promote the replica to a standalone instance
or delete it before starting the upgrade process.
If you delete it, be sure to recreate it after the source instance has upgraded to a different major version.
Aurora Step 4: Upgrade Aurora PostgreSQL secondary clusters
If you are using global DB clusters, make sure to upgrade the secondary clusters before the primary cluster.
This helps ensure that the primary and secondary are on the same major version. If you upgrade the primary first,
the secondary could still try to pull data over and could result in errors.
Aurora DB clusters that are configured as logical replication publishers or subscribers cannot undergo a major version upgrade.
Perform a Backup
You should always perform a backup as part of the preparation for a major upgrade.
This is the fifth step in the end-to-end process. A backup gives you a known restore point for your DB.
Step 5: Perform an Amazon RDS backup
In Amazon RDS, if your backup retention period is greater than 0,
the upgrade process creates DB snapshots of your DB instance before and after upgrading.
Update Extensions
Amazon RDS and Aurora users should update extensions before the major version upgrade.
This is also true if you plan to skip a major version with the upgrade.
For example, upgrading from versions 9.4.x, 9.5.x, or 9.6.x to version 11.x skips a major version.
There are other considerations with extensions if you skip a major version, which you will learn about in the next lesson.
Step 6: Update Amazon RDS extension
The extensions to update for Amazon RDS are:
Run the following command for each extension:
ALTER EXTENSION PostgreSQL-extension UPDATE TO 'new-version'
Step 6: Update Aurora extension
The extensions to be updated for Aurora are:
To learn more about upgrading extensions, review the following steps. To begin, select Start.
Upgrading extensions
Both Amazon RDS and Aurora will need special care when upgrading PostgreSQL extensions.
They have similar process steps for this segment of major upgrades.
Update an extension after an engine upgrade.
alter extension extension name update to 'new version'
A PostgreSQL engine upgrade doesn't upgrade any PostgreSQL extensions.
To update an extension after an engine upgrade, use the ALTER EXTENSION UPDATE command.
List currently installed extensions.
select * from pg_extension;
To list your currently installed extensions, use the PostgreSQL pg_extension catalog in the command shown.
View a list of specific extension versions.
select * from pg_available_extension_version;
To view a list of the specific extension versions that are available for your installation,
use the PostgreSQL pg_available_extension_versions view in the command shown.
Drop Extensions
Step 7: Drop extensions
A PostgreSQL engine upgrade doesn't upgrade any PostgreSQL extensions, so you must drop certain extensions before completing a major version upgrade.
Important facts about dropping extensions include the following:
1)Upgrading from versions 9.4.x, 9.5.x, or 9.6.x to version 11.x skips a major version, which means the pgRouting extension will not update. You can drop the pgRouting extension and then reinstall it to a compatible version after the upgrade.
2)The tsearch2 and chkpass extensions are no longer supported for PostgreSQL versions 11 or later. If you are upgrading to version 11.x or later, drop the tsearch2 and chkpass extensions before the upgrade.
Drop Unknown Data Types
Step 8: Drop unknown data types
PostgreSQL version 10 stopped supporting the 'unknown' data type. Therefore, you must drop unknown data types, depending on the target version. In PostgreSQL, you can drop columns using the 'unknown' data type. For version 10 and later, you must drop unknown data types to perform a major upgrade.
Example:
If a version 9.6 DB uses the 'unknown' data type, an upgrade to version 10 will show an error message such as the following:
Perform an Upgrade Dry Run
PostgreSQL recommends that you test a major version upgrade on a duplicate of your DB before attempting the upgrade on your production DB.
There are three ways that you can create a duplicate test instance:
- Restore your DB from a recent snapshot.
- Do a point-in-time restore of your DB to its latest restorable time.
- Clone your DB, for Aurora only.
Temporary names
During a major version upgrade, the public and template1 DBs and the public schema in every DB on the instance are temporarily renamed.
These objects appear in the logs with their original name and a random string appended. The string is appended so that custom settings such as locale and owner are preserved during the major version upgrade.
After the upgrade completes, the objects are renamed back to their original names.
An important note
During the major version upgrade process, you cannot complete a point-in-time restore of your instance.
After Amazon RDS or Aurora performs the upgrade, an automatic backup of the instance is created.
You can perform a point-in-time restore to times before the upgrade began and after the automatic backup of your instance has completed.
Resolve a Failed Upgrade
Step 10: Resolve a failed upgrade
Sometimes an upgrade fails. If an upgrade fails with precheck procedure errors, resolve the issues before you try again.
Precheck
During the major version upgrade process, Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL first runs a precheck procedure to identify any issues that might cause the upgrade to fail.
The precheck procedure checks all potential incompatible conditions across all DBs in the instance.
Issue encountered
If the precheck encounters an issue, it creates a log event indicating that the upgrade precheck failed.
The precheck process details are in an upgrade log named pg_upgrade_precheck.log for all the DBs of a DB instance.
Amazon RDS appends a timestamp to the file name.
You should resolve all the issues identified in the precheck log, and then retry the major version upgrade.
Upgrade the Production Instance
Step 11: Upgrade with confidence
When the dry run of your major version upgrade is successful, you should be able to upgrade your production database with confidence.
Post-Upgrade Activity
What's next
After an upgrade, complete these five steps. To review the steps, flip each of the following cards.
1) Review the same logs that pg_upgrade utility produces to ensure that the upgrade completed successfully.
2) Run the ANALYZE operation to refresh the pg_statistic table.
3) Confirm in the release notes which extensions you may need to upgrade.
4) Run the following command: ALTER EXTENSION PostgreSQL-extension UPDATE TO 'new-version'.
5) You can also upload the upgrade logs to Amazon CloudWatch Logs.
If your upgrade fails, restore the database to the time immediately prior to running the upgrade process. You can restore it using the console.
Amazon RDS users can find directions in the Amazon RDS
User Guide. For Aurora, you can restore a DB cluster to a specified time using the console. Directions can be found in the Aurora
User Guide.
Note : Times are shown in your local time zone, which is indicated by an offset from Universal Coordinated Time (UTC). For example, UTC-5 is Eastern Standard Time and Central Daylight Time.
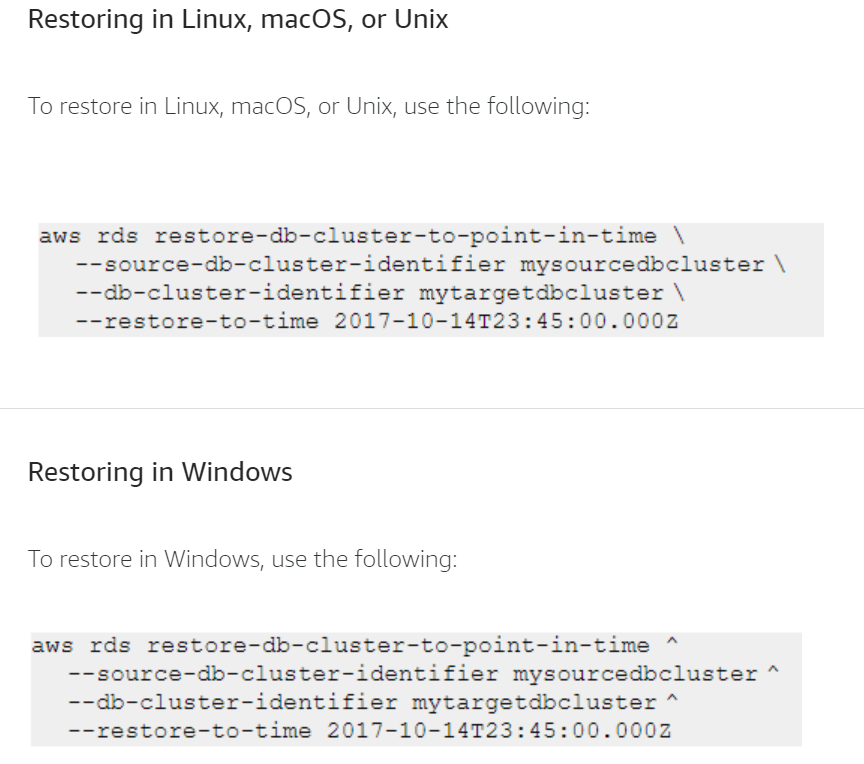
Restore using AWS Command Line Interface
Another option to restore a DB instance or cluster to a specified time is to use the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) command.
This applies to both Amazon RDS and Aurora.
restore-db-cluster-to-point-in-time
Select each + to learn more about how to restore a database instance using the AWS CLI command on select operating systems.
No comments:
Post a Comment